So you’re in the market for a new roof and want to know what options are out there. Well, look no further! In this article, we will explore the four basic roof types that every homeowner should be familiar with. Whether you’re looking for durability, aesthetics, or cost-effectiveness, we’ve got you covered. From the classic gable roof to the sleek and modern flat roof, you’ll discover the perfect option to suit your needs. So let’s dive right in and explore the wonderful world of roofs!
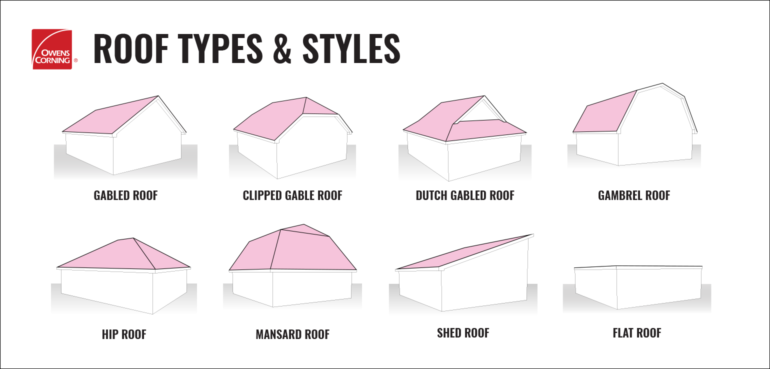
Gable Roof
Definition
A gable roof is one of the most common and recognizable roof types, characterized by its triangular shape. It consists of two sloping sides that meet at a ridge, forming a gable at each end of the house. This classic design allows for excellent water and snow runoff, making it highly efficient in areas with heavy precipitation.
Advantages
The gable roof offers several advantages that make it a popular choice for homeowners. Firstly, its simple design allows for ease of construction and lower costs compared to more complex roof styles. Additionally, the triangular shape provides ample attic space and allows for good ventilation, reducing the risk of moisture-related issues such as mold or rot. The steep slopes of a gable roof also make it highly resistant to high winds, making it suitable for areas prone to hurricanes or strong storms.
Disadvantages
While gable roofs have many advantages, they do come with a few drawbacks to consider. One of the main disadvantages is their vulnerability to strong crosswinds. The triangular shape can create uplift forces, causing the roof to become unstable during severe weather conditions. To mitigate this risk, it is important to ensure proper construction and reinforcement of the roof structure. Another potential disadvantage is the limited usable space in the attic due to the sloping sides, which may restrict storage or living space.
Hip Roof
Definition
A hip roof is characterized by its slopes on all four sides, meeting at a ridge to form a gentle slope or pyramid shape. This type of roof provides a visually pleasing appearance and enhanced stability. It is commonly used in both traditional and modern architecture.
Advantages
The hip roof offers several advantages that make it an appealing option for homeowners. Its sloping design provides excellent stability against high winds and prevents uplift forces, making it suitable for areas prone to hurricanes or severe storms. The four slopes of a hip roof also facilitate efficient water drainage, reducing the risk of leaks and water damage. Additionally, the broad eaves created by the extended slopes help protect the walls from weather elements and provide shade, reducing energy consumption for cooling purposes.
Disadvantages
One of the main drawbacks of hip roofs is their relatively complex design, which can lead to higher construction costs compared to simpler roof types. The multiple slopes also result in increased surface area, which may require more materials for roofing. Additionally, the inward slopes of a hip roof can limit the amount of usable attic or storage space. The complex structure may also pose challenges for roof maintenance and repairs.

Flat Roof
Definition
As the name suggests, a flat roof is a horizontal or near-horizontal roof surface. Unlike sloped roofs, the flat roof does not have any noticeable pitch or slope.
Advantages
Flat roofs offer several advantages that make them a popular choice for commercial buildings and modern homes. One of the main advantages is their affordability. The simple design and construction of a flat roof require fewer materials and labor, resulting in lower costs. The flat surface also provides additional usable space, allowing for rooftop gardens, solar panels, or outdoor recreational areas. Flat roofs are also easier to access, making maintenance and installation of equipment such as HVAC units or satellite dishes more convenient.
Disadvantages
While flat roofs have their benefits, they also come with some disadvantages. The main challenge with flat roofs is their susceptibility to water pooling. Without a slope to aid water drainage, flat roofs require proper installation of drainage systems to prevent water accumulation and potential leaks. The lack of pitch also means that debris, such as leaves or branches, may accumulate more easily on a flat roof, requiring regular maintenance to keep it clean. Additionally, the lack of slope can make flat roofs more vulnerable to structural damage caused by heavy snow accumulation or intense heat.
Mansard Roof
Definition
The mansard roof, also known as a French roof, is a four-sided roof with two distinct slopes, providing a unique and elegant appearance. The lower slope is steeper and more vertical, while the upper slope is shallower.
Advantages
The mansard roof offers both aesthetic and functional advantages. From an aesthetic standpoint, its elegant design adds charm and character to the building, making it a popular choice for historic or Victorian-style homes. The two slopes of a mansard roof also provide additional living space in the attic, making it suitable for those who desire extra room without the need for a full story addition. The steep lower slope also offers enhanced rainwater runoff, reducing the risk of leaks and water damage.
Disadvantages
The complexity of the mansard roof design can result in higher construction and maintenance costs. The two slopes require more materials and labor compared to simpler roof types, which can make it a pricier option. Additionally, the complexity of the roof structure can make repairs and maintenance more challenging. The unique design of the mansard roof can also limit its suitability for areas with heavy snowfall, as the steep lower slope may present challenges in snow removal.

Gambrel Roof
Definition
The gambrel roof is characterized by its symmetrical two-sided design, with two slopes on each side. The upper slope is less steep than the lower slope, creating a distinctive barn-like appearance.
Advantages
The gambrel roof offers both practical and aesthetic advantages. Its design allows for maximum usable space in the attic or upper floor, making it ideal for those who require additional living or storage space. The steep lower slope also facilitates effective water runoff, minimizing the risk of leaks and water damage. The gambrel roof design is particularly suitable for homeowners looking for a traditional or rustic aesthetic, reminiscent of barns and colonial-style architecture.
Disadvantages
One of the main drawbacks of the gambrel roof is its lack of resistance against high winds. The multiple slopes and overhangs can create uplift forces, making it more susceptible to wind damage. Reinforcement and proper installation techniques are crucial when constructing a gambrel roof to ensure its stability in areas prone to storms. Additionally, the complexity of the gambrel roof design can result in higher construction costs and potentially more challenging maintenance or repairs.
Saltbox Roof
Definition
The saltbox roof is a long, sloping roof with one side significantly longer than the other. Its distinct shape resembles the traditional wooden box used for storing salt, hence the name.
Advantages
The saltbox roof offers several advantages that make it a unique and appealing choice. Its asymmetrical design adds visual interest to the building’s exterior, creating a characteristic and eye-catching look. The long slope of the roof provides efficient water drainage, reducing the risk of leaks and water damage. The saltbox roof is also compatible with various architectural styles, blending well with both historic and contemporary homes.
Disadvantages
The longer side of the saltbox roof can present challenges in terms of construction and maintenance. The increased surface area may require additional materials and labor, potentially increasing costs. The asymmetrical design can also result in uneven weight distribution, requiring proper structural support and reinforcement. Additionally, the unique shape of the saltbox roof can limit the amount of usable interior space or storage options.

Butterfly Roof
Definition
The butterfly roof is a unique and modern roof design characterized by its inverted V-shape, resembling the wings of a butterfly. The two roof surfaces slope inward, creating a central valley.
Advantages
The butterfly roof offers several advantages in terms of both aesthetics and functionality. Its distinctive design adds a contemporary and architectural focal point to the building’s exterior, making it a popular choice among creative homeowners. The inverted V-shape of the roof also allows for efficient rainwater collection, making it compatible with rainwater harvesting systems. The central valley created by the two slopes can be used for skylights or windows, bringing abundant natural light into the interior spaces.
Disadvantages
The unique design of the butterfly roof requires careful consideration during construction. Its inverted V-shape can make it more vulnerable to water leakage if not properly sealed or installed. The central valley can also pose challenges in terms of maintenance, as debris can accumulate in that area, requiring regular cleaning. Additionally, the asymmetric design of the butterfly roof may limit its compatibility with certain architectural styles, making it more suitable for contemporary or modern homes.
Skillion Roof
Definition
The skillion roof, also known as a shed roof or mono-pitched roof, is characterized by its single sloping surface. It typically has a steeper slope on one side, providing a dynamic and modern appearance.
Advantages
The skillion roof offers several advantages that make it an appealing choice for homeowners seeking a contemporary aesthetic. Its clean lines and simple design make it suitable for both residential and commercial buildings. The single slope allows for efficient water runoff, reducing the risk of leaks and water damage. The skillion roof is also versatile in terms of orientation, as it can be angled to optimize solar energy collection for homes with solar panels.
Disadvantages
One of the main disadvantages of the skillion roof is its limited interior space. The steep slope of the roof restricts the usable attic or storage space, which may be a consideration for homeowners with specific spatial needs. Additionally, the skillion roof design may require additional insulation and waterproofing measures compared to more traditional roof types, as it is more exposed to the elements. The unique design of the skillion roof may also limit its compatibility with certain architectural styles, as it is more commonly associated with modern or minimalist designs.

Curved Roof
Definition
The curved roof, also referred to as an arched roof or barrel roof, features a convex curve along its length. This distinctive design provides a visually striking and unconventional roof shape.
Advantages
The curved roof offers several advantages that make it an appealing option for those seeking a unique architectural style. Its distinctive shape adds character and visual interest to the building’s exterior, making it a focal point and conversation starter. The curved form of the roof also allows for efficient water drainage, minimizing the risk of leaks and water damage. The curved design can also enhance the overall structural integrity of the building, providing better resistance against heavy winds or snow loads.
Disadvantages
The complexity of constructing a curved roof can result in higher costs compared to simpler roof designs. The curved shape requires precise engineering and specialized construction techniques, which may require additional time and expertise. The unique design also presents challenges in terms of maintenance and repairs, as finding compatible roofing materials or navigating the curved surface may be more difficult. Additionally, the curved roof’s unconventional shape may limit its compatibility with standard windows or fittings, requiring custom-made solutions.
Shed Roof
Definition
The shed roof, also known as a mono-pitched roof or lean-to roof, is a single sloping roof surface that is attached to a taller wall or higher roof.
Advantages
The shed roof offers several advantages that make it a practical and cost-effective option for various structures. Its simple and functional design allows for efficient rainwater runoff, minimizing the risk of leaks or water damage. The single slope also makes the shed roof easy to construct, requiring fewer materials and labor compared to more complex roof styles. The shed roof is particularly suitable for extensions or additions to existing buildings, providing a seamless and complementary integration to the main structure.
Disadvantages
One of the main disadvantages of the shed roof is its limited interior space. The single slope can restrict the usable attic or storage space compared to roofs with a steeper pitch. The shed roof’s low slope may also restrict the use of windows or skylights, limiting the amount of natural light that can enter the interior spaces. Additionally, the shed roof’s asymmetrical design may not be suitable for certain architectural styles, as it is commonly associated with more utilitarian or modern designs.
In conclusion, each of the 10 roof types discussed in this article offers its own unique features, advantages, and disadvantages. From the classic gable roof to the unconventional butterfly roof, homeowners have various options to choose from based on their personal preferences, architectural style, and environmental considerations. Whether it’s for aesthetics, functionality, or cost-effectiveness, understanding the characteristics of each roof type can help you make an informed decision when it comes to selecting the perfect roof for your home.